Understanding Michigan state tax rate is crucial for anyone living, working, or doing business in the state. Whether you're a resident, entrepreneur, or investor, staying informed about tax obligations ensures compliance and better financial planning. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about Michigan's state tax system, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and more.
Taxes are an essential part of life, and knowing the specifics of Michigan's tax structure can save you time, money, and potential legal trouble. This article will provide a detailed overview of the various tax rates and regulations that apply to residents and businesses in Michigan.
From sales tax to property tax, Michigan's tax system is designed to fund public services and infrastructure. By understanding the nuances of these tax rates, you'll be better equipped to manage your finances effectively and make informed decisions. Let's dive into the details.
Read also:Unlock The Secrets Of Your November 11 Star Sign A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Biography of Michigan State Tax System
- Michigan Income Tax Rate
- Michigan Sales Tax Rate
- Michigan Property Tax Rate
- Michigan Business Tax Rate
- Deductions and Credits in Michigan
- Filing Michigan State Taxes
- Penalties for Late Payment
- Useful Resources for Michigan Taxpayers
- Conclusion
Biography of Michigan State Tax System
Overview of Michigan's Tax Structure
Michigan's tax system is designed to generate revenue for the state's various public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, and public safety. The state imposes several types of taxes, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business tax.
Residents and businesses in Michigan are required to pay these taxes based on their income, purchases, property ownership, and business activities. Understanding the tax structure is essential for ensuring compliance and optimizing financial planning.
Michigan Income Tax Rate
The Michigan state income tax rate is a flat rate of 4.25% for most taxpayers. This rate applies to taxable income earned by individuals, trusts, and estates. Unlike some states that have progressive tax brackets, Michigan's flat tax rate simplifies the calculation process for taxpayers.
For example, if you earn $50,000 in taxable income, your Michigan state income tax would be $2,125 (4.25% of $50,000). This rate has remained consistent for several years, providing stability for taxpayers.
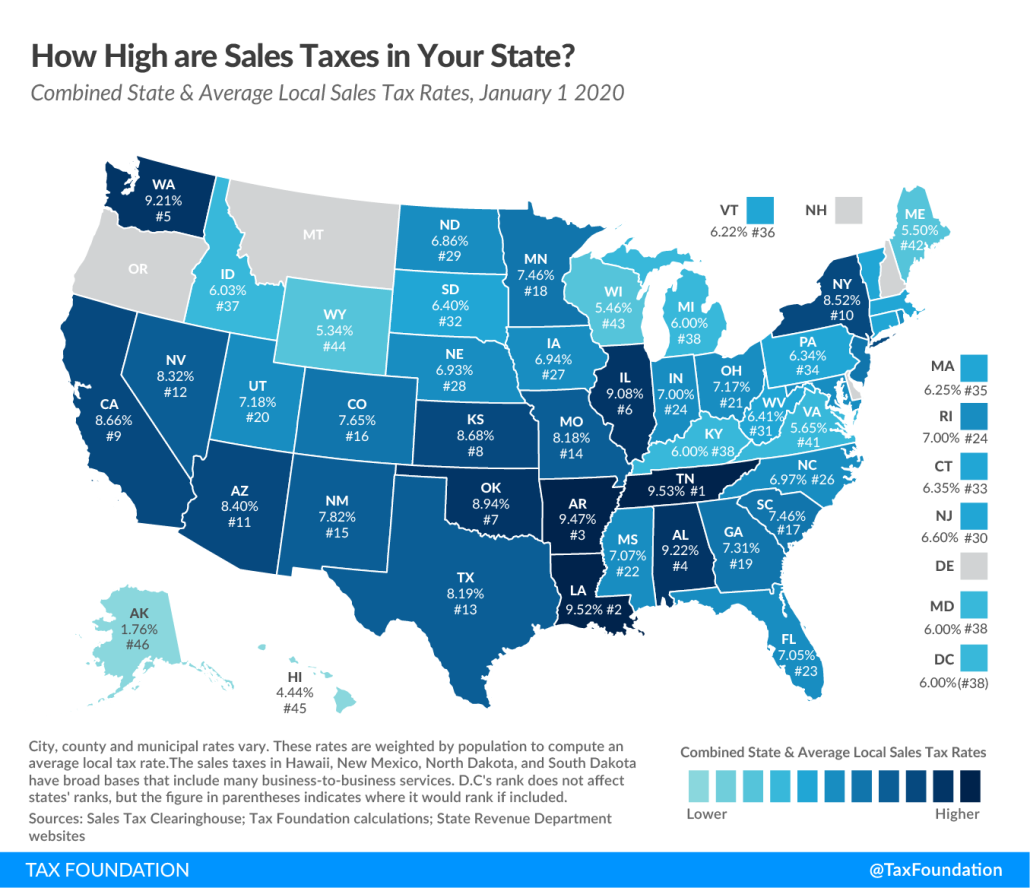
Michigan Sales Tax Rate
Statewide Sales Tax
Michigan's statewide sales tax rate is 6%. This tax applies to most retail purchases, including goods and services. However, certain items, such as groceries and prescription medications, are exempt from sales tax. It's important to note that local jurisdictions may impose additional sales taxes, which can increase the total rate in some areas.
For instance, if you purchase an item priced at $100, the sales tax would be $6 (6% of $100). If there is an additional local sales tax of 1%, the total tax would be $7 (6% + 1%).
Read also:The Crown Characters Season 1 A Deep Dive Into The Iconic Cast And Their Roles
Michigan Property Tax Rate
Overview of Property Tax
Property tax in Michigan is assessed based on the property's taxable value and the millage rate. The taxable value is determined by the local assessor and is typically lower than the market value. The millage rate varies depending on the local taxing jurisdiction and is expressed in mills (1 mill = $1 per $1,000 of taxable value).
For example, if your property has a taxable value of $100,000 and the millage rate is 20 mills, your property tax would be $2,000 (20 mills x $100,000).
Michigan Business Tax Rate
Corporate Income Tax
Michigan imposes a corporate income tax rate of 6% on the taxable income of corporations. This tax applies to both C corporations and S corporations. Additionally, businesses may be subject to other taxes, such as the Michigan Business Tax (MBT), depending on their structure and activities.
For example, if a corporation earns $100,000 in taxable income, the Michigan corporate income tax would be $6,000 (6% of $100,000).
Deductions and Credits in Michigan
Common Deductions
Michigan offers several deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their tax liability. Some of the most common deductions include:
- Standard deduction for individuals and families
- Itemized deductions for mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable contributions
- Educator expense deduction for teachers
Additionally, Michigan offers various credits, such as the Homestead Property Tax Credit, which helps homeowners offset their property tax burden.
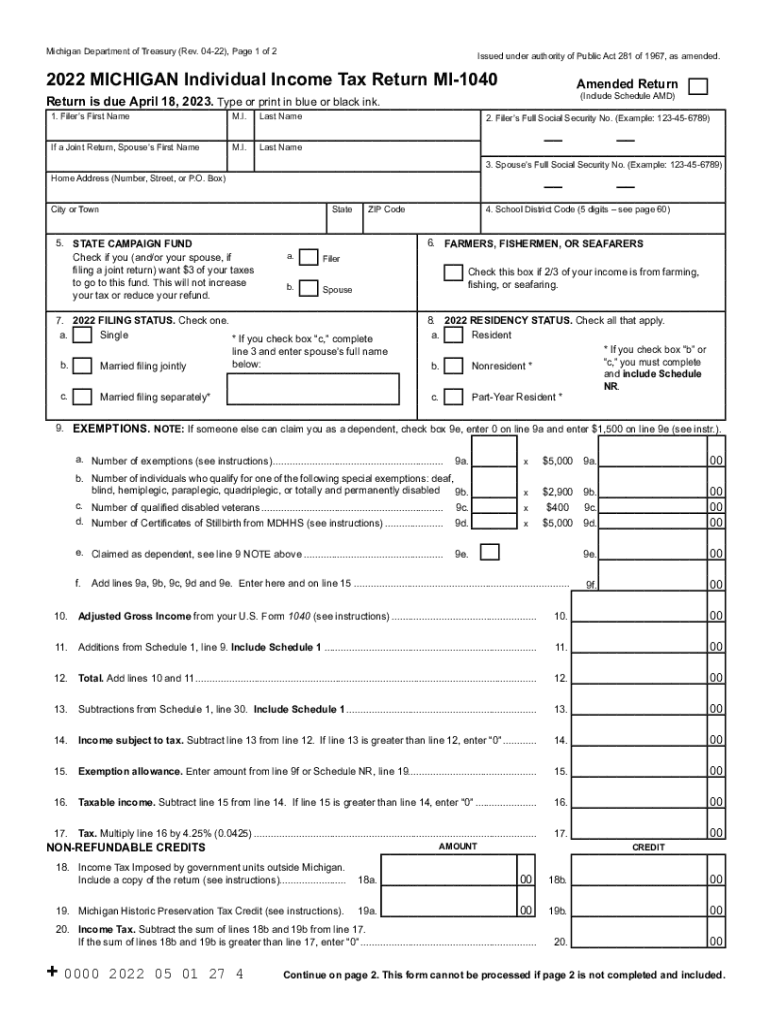
Filing Michigan State Taxes
Steps to File Your Taxes
Filing Michigan state taxes can be done electronically or by mail. The Michigan Department of Treasury provides resources and tools to assist taxpayers in completing their returns accurately and efficiently. Here are the steps to file your Michigan state taxes:
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, and other income statements.
- Calculate your taxable income and determine any deductions or credits you qualify for.
- Complete the Michigan Individual Income Tax Form (MI-1040).
- Submit your completed form electronically or by mail by the deadline, which is typically April 15th.
Penalties for Late Payment
Consequences of Missing the Deadline
Failing to file or pay your Michigan state taxes on time can result in penalties and interest. The penalty for late filing is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest is charged on the unpaid tax at a rate of 1.5% per month or part of a month.
To avoid penalties, it's important to file and pay your taxes by the deadline or request an extension if needed.
Useful Resources for Michigan Taxpayers
Where to Find Help
Michigan taxpayers have access to several resources to help them understand and comply with state tax laws. Some of the most useful resources include:
- Michigan Department of Treasury: Provides information on state tax laws, forms, and filing procedures.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS): Offers guidance on federal tax laws and how they interact with state taxes.
- Tax professionals and accountants: Can provide personalized advice and assistance with tax preparation and planning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Michigan state tax rate is essential for anyone living or doing business in the state. By familiarizing yourself with the various tax rates and regulations, you can ensure compliance and optimize your financial planning. From income tax to property tax, Michigan's tax system is designed to fund public services and infrastructure, making it an important aspect of daily life for residents and businesses.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax obligations, utilizing available deductions and credits, and seeking professional help if needed. Don't forget to share this article with others who may find it helpful and explore more resources on our website for additional information.
Data Sources:
- Michigan Department of Treasury
- Internal Revenue Service
- U.S. Census Bureau