Understanding the average distance between Mars and Earth is crucial for space exploration, scientific research, and astronomical studies. As our fascination with the Red Planet grows, so does the need to comprehend its proximity to our home planet. This article delves into the complexities of the Mars-Earth average distance, providing insights that are both informative and scientifically accurate.
The relationship between Mars and Earth is dynamic, with their distance constantly changing due to their elliptical orbits. This variability makes it essential to explore the concept of "average distance" to gain a clearer understanding of their celestial connection. By examining this topic, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities in interplanetary travel.
This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the average distance between Mars and Earth, incorporating scientific data, expert insights, and practical applications. Whether you're a space enthusiast or a professional astronomer, this guide will offer valuable information to enhance your knowledge of this fascinating subject.
Read also:Paris Jackson The Story Behind Michael Jacksons Daughter And Her Tattoos
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Mars-Earth Distance
- Understanding the Orbits of Mars and Earth
- How to Calculate the Mars-Earth Average Distance
- Closest and Farthest Distances Between Mars and Earth
- Scientific Significance of Mars-Earth Distance
- Impact on Space Exploration
- Historical Data on Mars-Earth Distance
- Technological Advances in Measuring Distance
- Future Prospects for Mars Missions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Mars-Earth Distance
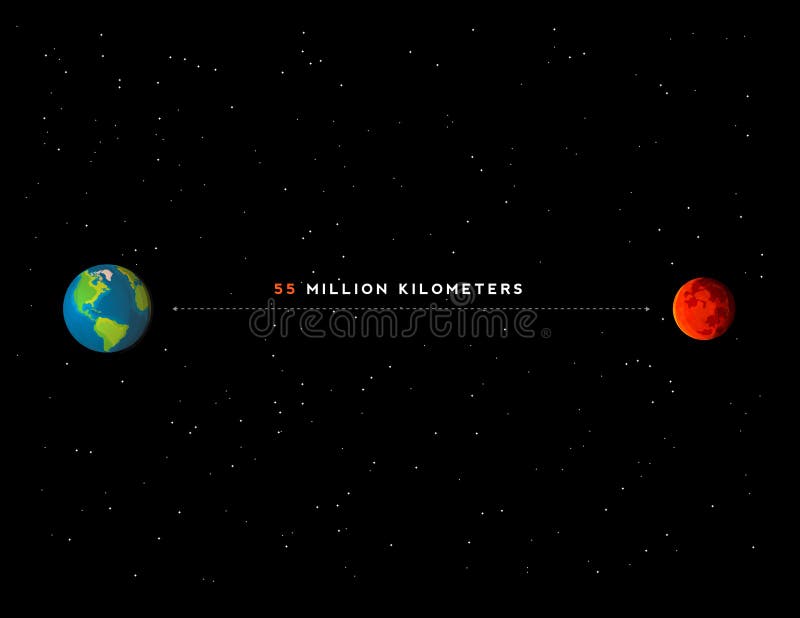
The average distance between Mars and Earth is a critical parameter in astronomy, influencing everything from space missions to planetary observations. The distance varies significantly due to the elliptical nature of both planets' orbits. At its closest, Mars can be approximately 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles) away from Earth, while at its farthest, the distance can stretch to about 401 million kilometers (249 million miles).
Why is the Mars-Earth Distance Important?
Understanding the average distance between Mars and Earth is vital for several reasons:
- It affects the planning and execution of space missions.
- It impacts communication delays between Earth and Mars-based spacecraft.
- It influences the design of spacecraft and their propulsion systems.
Understanding the Orbits of Mars and Earth
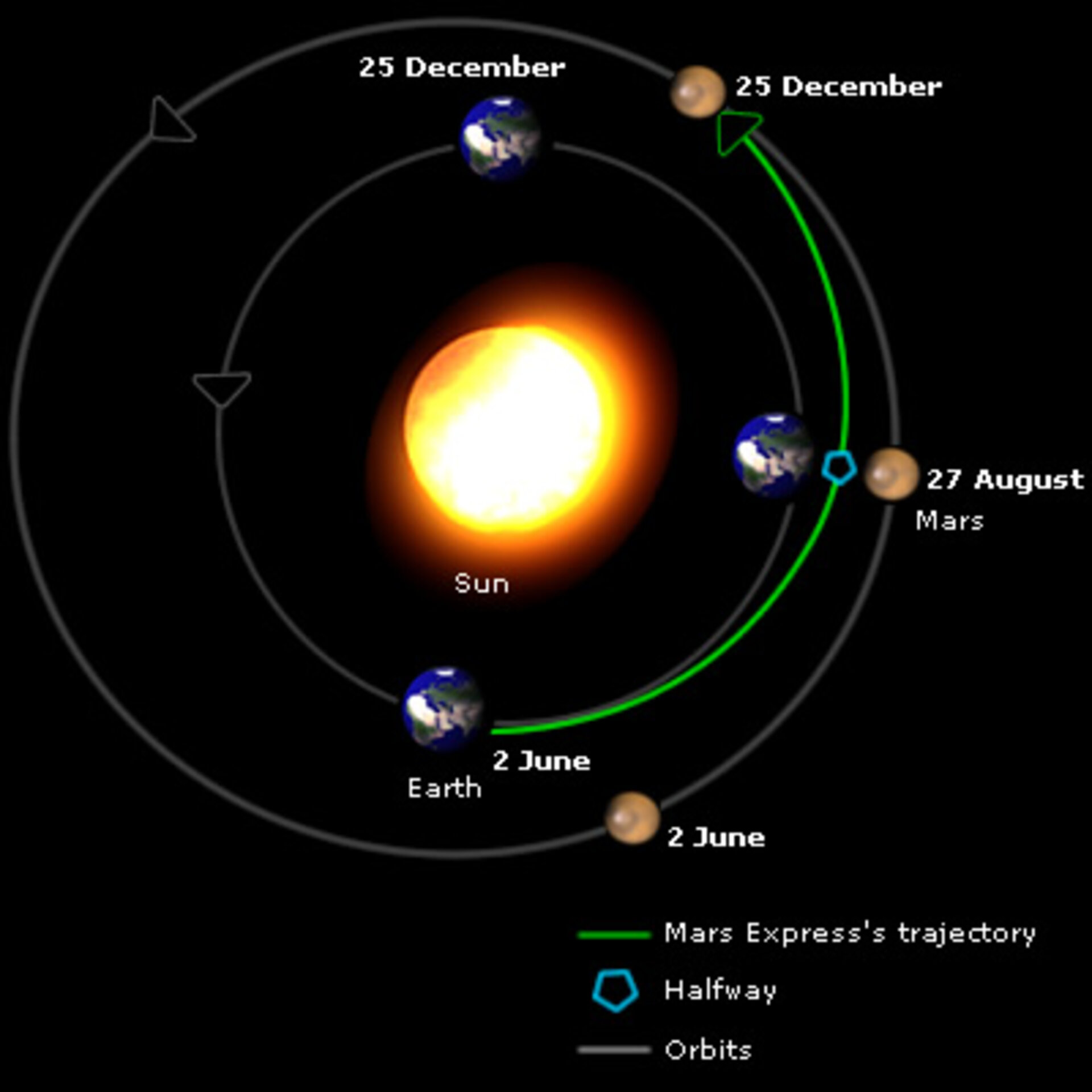
Both Mars and Earth orbit the Sun in elliptical paths, with Earth closer to the Sun than Mars. This difference in orbital paths results in varying distances between the two planets. Earth completes one orbit around the Sun in about 365.25 days, while Mars takes approximately 687 Earth days.
Elliptical Orbits and Their Impact
The elliptical shape of the orbits means that the distance between Mars and Earth is not constant. When the two planets are on the same side of the Sun and aligned, they are at their closest point, known as "opposition." Conversely, when they are on opposite sides of the Sun, they are at their farthest point, called "conjunction."
How to Calculate the Mars-Earth Average Distance
The average distance between Mars and Earth is calculated using the semi-major axes of their orbits. The semi-major axis of Earth's orbit is about 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles), while Mars' semi-major axis is approximately 227.9 million kilometers (141.6 million miles). The average distance is derived from these values and the relative positions of the planets.
Using Astronomical Units (AU)
Astronomers often use Astronomical Units (AU) to measure distances within the solar system. One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun. Mars is, on average, about 1.52 AU from the Sun, making its average distance from Earth approximately 1.52 AU.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Rent Collection Services In Dc Metro
Closest and Farthest Distances Between Mars and Earth
The closest approach of Mars to Earth, known as "perihelic opposition," occurs when Mars is at its closest to the Sun and aligned with Earth. During this event, the distance between the two planets can be as little as 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles). Conversely, the farthest distance, or "aphelic conjunction," can reach up to 401 million kilometers (249 million miles).
Factors Affecting Distance Variability
Several factors contribute to the variability in Mars-Earth distance:
- The elliptical shape of both planets' orbits.
- The relative positions of the planets in their orbits.
- The gravitational influence of other celestial bodies.
Scientific Significance of Mars-Earth Distance
The distance between Mars and Earth has significant implications for scientific research. It affects the accuracy of telescopic observations, the timing of space missions, and the study of Mars' atmosphere and geology. Understanding this distance helps scientists plan experiments and develop technologies for interplanetary exploration.
Applications in Astronomy
Knowledge of the Mars-Earth average distance is essential for:
- Tracking the movement of Mars in the night sky.
- Calculating the speed and trajectory of spacecraft traveling to Mars.
- Studying the effects of distance on radio wave communication.
Impact on Space Exploration
Space agencies like NASA and ESA rely heavily on accurate calculations of the Mars-Earth distance to plan missions. The timing of launches is critical, as it determines the energy required for spacecraft to reach Mars. The "launch window" occurs when the planets are favorably aligned, minimizing fuel consumption and travel time.
Challenges in Mars Missions
Despite advancements in technology, several challenges remain:
- Long travel times due to the vast distance.
- Communication delays caused by the distance.
- Environmental conditions on Mars that affect landing and operations.
Historical Data on Mars-Earth Distance
Throughout history, astronomers have made significant strides in measuring the distance between Mars and Earth. Early observations relied on trigonometric parallax, while modern techniques use radar and spacecraft telemetry. These efforts have led to increasingly precise measurements, enhancing our understanding of the solar system.
Key Milestones in Distance Measurement
Some notable milestones include:
- The first accurate measurement by Giovanni Cassini in the 17th century.
- The use of radar in the 20th century to refine distance calculations.
- The deployment of spacecraft to provide direct measurements.
Technological Advances in Measuring Distance
Modern technology has revolutionized the way we measure the Mars-Earth distance. Techniques such as Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) and laser ranging provide unprecedented accuracy. These methods are crucial for tracking spacecraft and ensuring the success of interplanetary missions.
Future Innovations
Future innovations in distance measurement may include:
- Improved radar systems with higher precision.
- Advanced telescopes capable of observing Mars in greater detail.
- Spacecraft equipped with cutting-edge navigation systems.
Future Prospects for Mars Missions
As humanity continues to explore Mars, the importance of understanding the average distance between the two planets will only grow. Future missions aim to establish permanent bases on Mars, requiring precise calculations of distance and travel time. These efforts will pave the way for a new era of space exploration.
Human Missions to Mars
Human missions to Mars present unique challenges, including:
- Ensuring the safety of astronauts during long journeys.
- Developing life support systems for extended stays on Mars.
- Addressing the psychological effects of isolation and distance from Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the average distance between Mars and Earth is a fundamental concept in astronomy and space exploration. By understanding this distance, we can better plan missions, conduct research, and advance our knowledge of the solar system. As technology continues to evolve, our ability to measure and utilize this distance will improve, opening new possibilities for interplanetary exploration.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. For more fascinating articles on space and astronomy, explore our website and stay updated on the latest developments in the field.
Data and references for this article were sourced from reputable organizations such as NASA, ESA, and scientific journals, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.